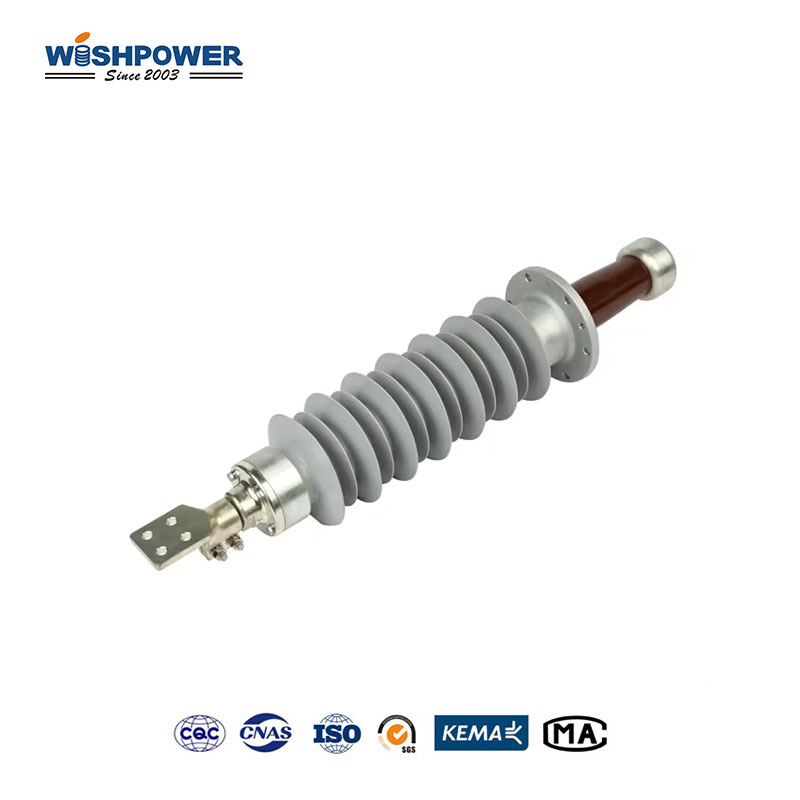
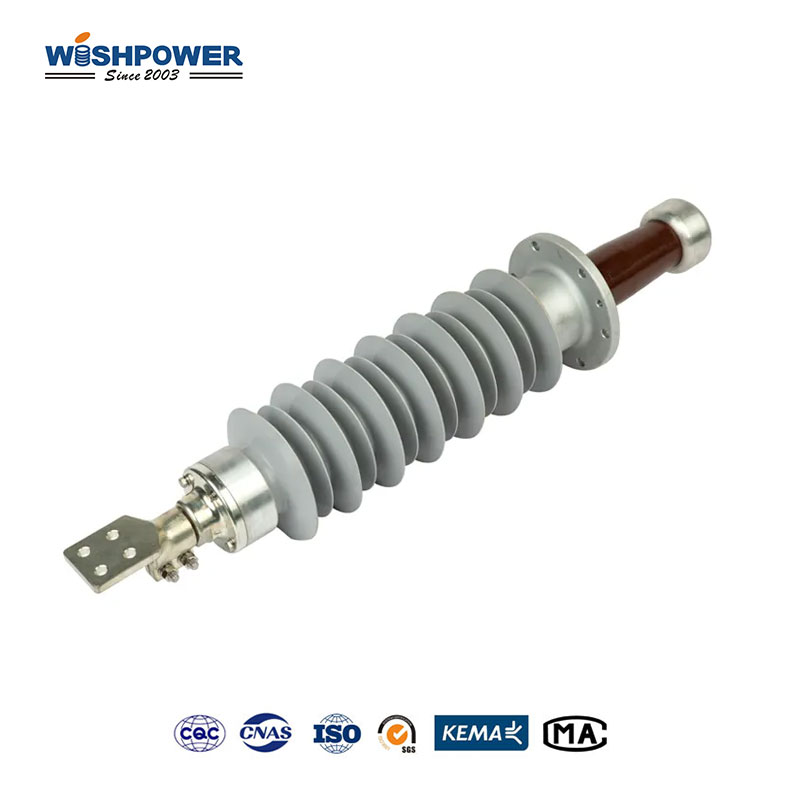
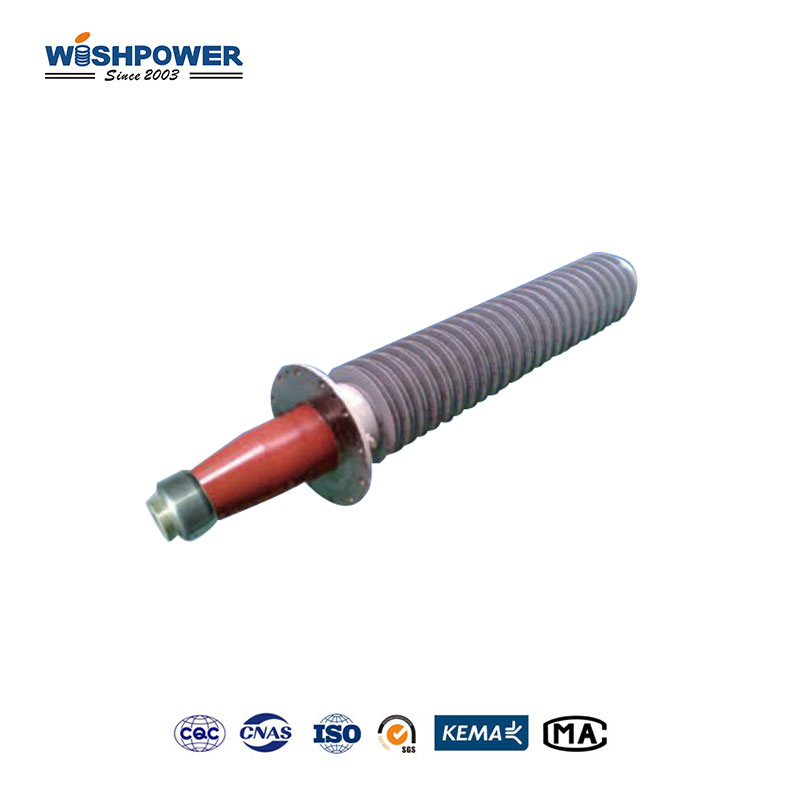
Transformers enable electrical systems to accomplish high or low-voltage level changes for effective transmission and distribution network operations. The transformer requires bushings as essential parts that enable safe conduit passage of electrical conductors through the tank while offering insulation and mechanical reinforcement. Within the transformer framework, bushings exist in two principal types which are High Voltage (HV) bushings and Low Voltage (LV) bushings.
What is a Bushing?
The electrical equipment containing transformers along with circuit breakers and switchgear use bushings as insulation devices. The insulation device creates a protected channel for electrical conductors to move through transformer metal containers. Through its isolative properties, the bushing protects energized transformer parts against external electrical faults as well as arcing and short circuits.
Transformers install either HV (High Voltage) or LV (Low Voltage) bushings according to their intended voltage system specifications. The main functions are shared between bushings but their designs follow different approaches to deal with different electrical and mechanical strains.
What is HV (High Voltage) Bushing?
The power system connects through an HV bushing to the internal high-voltage transformer section of power transformers. These bushings maintain the high electrical stress capacity which powers transmission at various kilovoltage (kV) and hundred kilovoltage ranges.
Key Functions of HV Bushings:
The primary function of an HV bushing exists in its role to insulate the high-voltage conductor from contact with the transformer casing or tank. The materials used for insulation in HV bushings need to demonstrate strong dielectric properties because they operate under high-voltage conditions.
Digital Support for High-Voltage Conductors is one of the primary functions of HV bushings. The installations keep the conductors stationary and safeguard the transformer against potential damage.
The special structure design of HV bushings enables an even distribution of voltage stress from end to end. Preventing electrical breakdowns and flashovers which would cause transformer damage remains vital for proper operation.
What is LV (Low Voltage) Bushing?
The low-voltage transformer section of the electrical grid gets its connection through an LV bushing. These bushings operate within a voltage range of hundred volts up to tens of kilovolts.
Key Functions of LV Bushings:
Just like HV bushings LV bushings serve to insulate the low-voltage conductor by maintaining an electrical gap between it and the transformer metal tank or shell. Sufficient insulation must exist on low-voltage side conductors to withstand the voltage level without dysfunctional operation.
Low-voltage bushings provide support for electrical conductors as well as alignment functions that secure proper connections to the transformer.
The safe operation of transformers depends on voltage stability even though low-voltage bushings work with less power than their high voltage counterparts.
Differences Between HV and LV Bushings
The main function of HV and LV bushings remains the same but their structural composition along with voltage-handling capabilities show fundamental variations.
Voltage rating stands out as the most important distinction between the two types of bushings. The voltage handling capability of HV bushings extends beyond 100 kV which makes them different from LV bushings that operate at less than 30 kV.
The physical dimensions of HV bushings expand to accommodate their requirements of managing both electrical and mechanical strains during high-voltage operations. The structure of LV bushings remains simple and they possess smaller dimensions.
The manufacturing materials for HV bushings incorporate high dielectric strength materials such as porcelain or composite materials or oil-impregnated paper but LV bushings commonly utilize epoxy resin or silicone rubber for their composition.
Total investment in cooling technology varies between HV and LV bushings since HV bushings need oil-based cooling solutions or other devices to handle excessive high-voltage heat whereas LV bushings function without these added systems.
HV bushings feature higher prices and need increased scheduled maintenance compared to LV bushings because their size is bigger along with their complex materials and strict performance specifications.
What is hv and lv bushing in transformer?
The insulation and mechanical support for electrical conductors in transformers depends on HV and LV bushings which enable safe transmission through the transformer casing. The transformer’s high-voltage side utilizes HV bushings to provide resilient insulation and voltage stress control while LV bushings manage transmission of electrical energy at lower voltages appearing on the transformer’s low-voltage side.
If you have different opinions or want to know more, please leave a message on the website or contact us directly at info@wishpower.net

















